What is the phase diagram of water? Socratic
Phase diagram of water Note: for H2O melting point decreases with increasing pressure, for CO2 melting point increases with increasing pressure. WATER Covers ~ 70% of the earth's surface Life on earth depends on water Water is a "universal" solvent Easily polluted; hard to purify.
12.7 Phase Diagrams Chemistry LibreTexts
This chemistry video tutorial explains the concepts behind the phase diagram of CO2 / Carbon Dioxide and the phase diagram of water / H2O. This video contai.

—Phase diagram of water Download Scientific Diagram
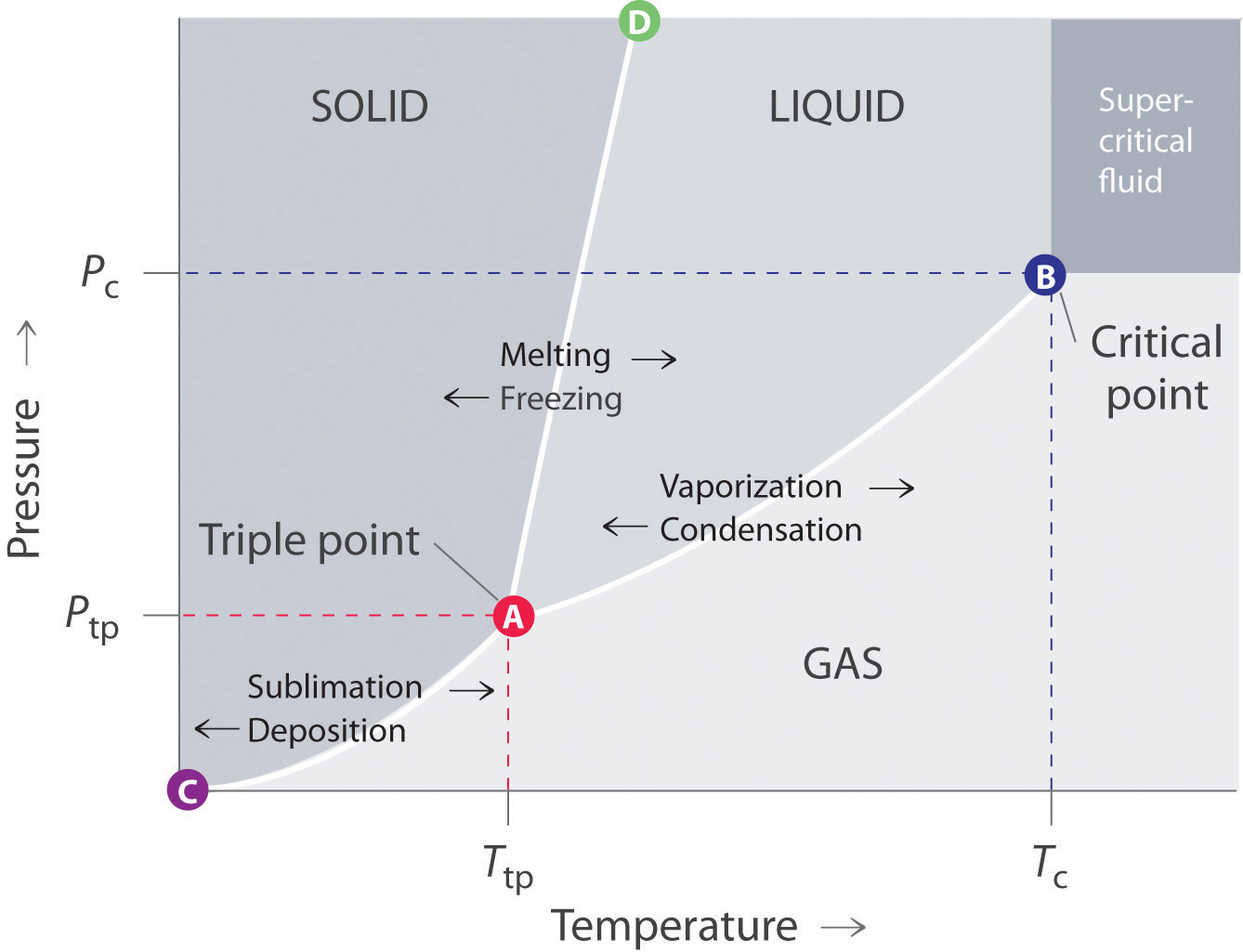
Example 12.4.1 12.4. 1: Water. Referring to the phase diagram of water in Figure 12.4.2 12.4. 2: predict the physical form of a sample of water at 400°C and 150 atm. describe the changes that occur as the sample in part (a) is slowly allowed to cool to −50°C at a constant pressure of 150 atm.

The phase diagram of water ((© ChemWiki (© UC Davis, Wikimedia Commons) Download Scientific
Phase diagram for ammonium nitrate and water binary mixture. Above the blue curve is the liquid state, while below is the solid state. Crystals and Polymorphs. Crystalline solids can have multiple possible structures, dependent on thermodynamic variables. This is why you may hear someone talk about different forms of ice, such as ice II, ice.

Phase Diagrams of Water 101 Diagrams
An Efficient Way to Predict Water's Phases. A machine-learning technique maps water's phase space as reliably as gold standard ab initio calculations but at a much smaller computational cost. Given its familiarity, water is a surprisingly tricky substance to simulate. In addition to having liquid and gas phases, water adopts at least 14.

Phase Diagram of Water Explanation and Diagrammatic Representation of Phase Diagram of Water
Simplified temperature/pressure phase change diagram for water. The pressure on a pressure-temperature diagram (such as the water phase diagram shown above) is the partial pressure of the substance in question.. A phase diagram in physical chemistry, engineering, mineralogy, and materials science is a type of chart used to show conditions (pressure, temperature, volume, etc.) at which.

Phase Diagram
Depiction in Phase Diagram of Water. At different temperatures and pressures, a phase diagram depicts the preferred physical states of matter. Water is a liquid at typical room temperatures and pressures, but it becomes solid (i.e. ice) if the temperature is reduced below 273 K, and gaseous (i.e. steam) if the temperature is increased above 373 K at the same pressure.
.PNG)
Phase Diagrams Presentation Chemistry
The phase diagrams calculated at the classical level with DNN@MB-pol (a) and MB-pol (b), and at the quantum level with MB-pol (c) are compared with the experimental phase diagram (d).The.
PPT Chapter 11. States of Matter PowerPoint Presentation, free download ID1831358
Consider the phase diagram for carbon dioxide shown in Figure \(\PageIndex{5}\) as another example. The solid-liquid curve exhibits a positive slope, indicating that the melting point for CO 2 increases with pressure as it does for most substances (water being a notable exception as described previously). Notice that the triple point is well above 1 atm, indicating that carbon dioxide cannot.

Schematic water phase diagram. Below the critical point, that is 374 K... Download Scientific
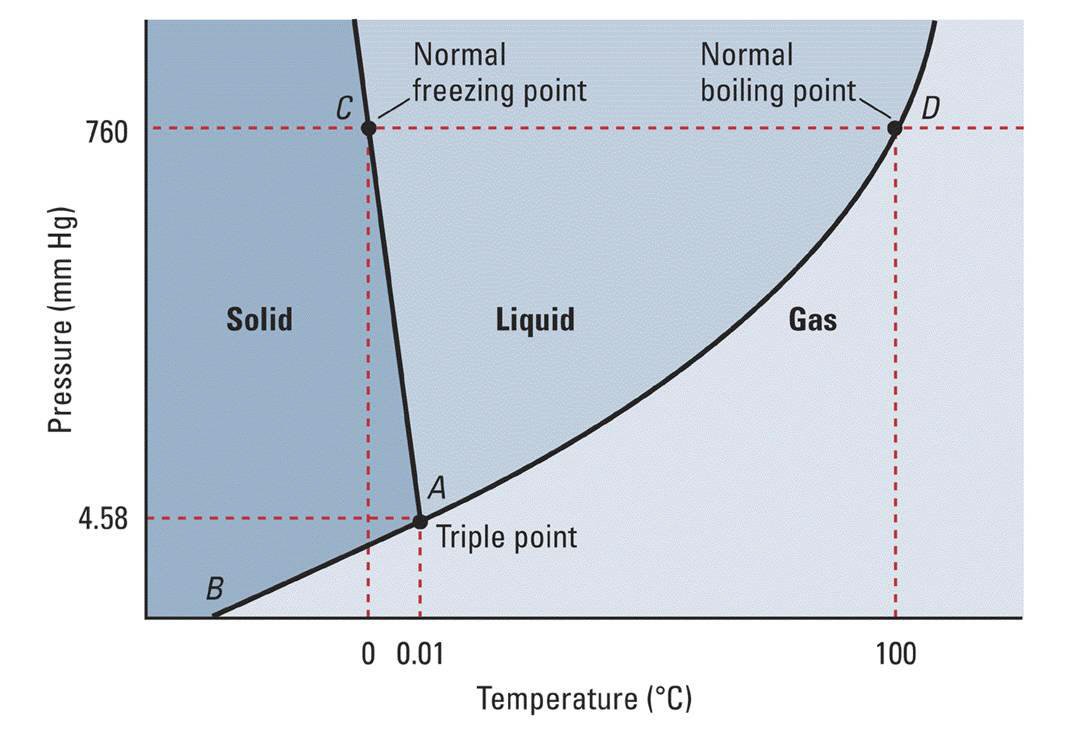
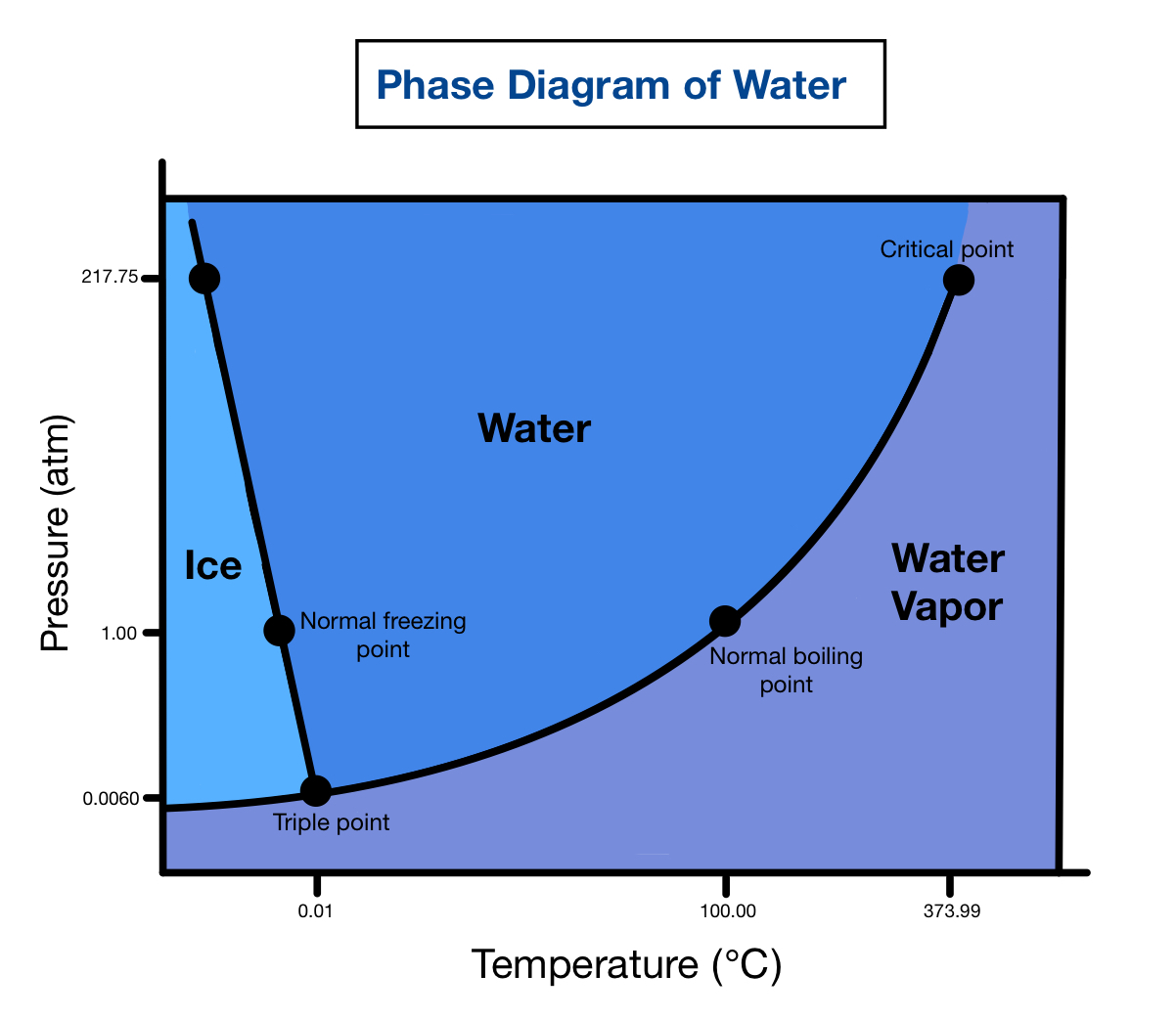
The phase diagram for water is shown in the figure below. Figure 13.20. 1: Phase diagram for water. Notice one key difference between last section's general phase diagram, and the above phase diagram for water: in water's diagram, the slope of the line between the solid and liquid states is negative rather than positive.

physical chemistry Why does increase in pressure favor formation of water in waterice
In the video here, Sal uses a horizontal line through the phase diagram. But, it doesn't have to be horizontal. Imagine a vertical line through this diagram-- for water, choose 100 degrees C. As long as you are at 100 C, you can change the phase by changing the pressure on the system.

Phase Diagram of Water (H2O)
We can use the phase diagram to identify the physical state of a sample of water under specified conditions of pressure and temperature. For example, a pressure of 50 kPa and a temperature of −10 °C correspond to the region of the diagram labeled "ice.". Under these conditions, water exists only as a solid (ice).
Phase Change Diagram of Water — Overview & Importance Expii
The phase diagram for water is shown in the Figure below . Figure 13.26. Phase diagram for water. Notice one key difference between the general phase diagram and the phase diagram for water. In water's diagram, the slope of the line between the solid and liquid states is negative rather than positive. The reason is that water is an unusual.

thermodynamics Vacuum freezing of water Physics Stack Exchange
The AB line is the ice-vapor line, the BC line is the ice-water line, and the BD line is the water-vapor line. We can use the phase diagram to identify the state where water exists under specific temperature and pressure conditions. For example, water is ice at 50 kPa and - 10 o C.

Phase diagram of pure water Download Scientific Diagram
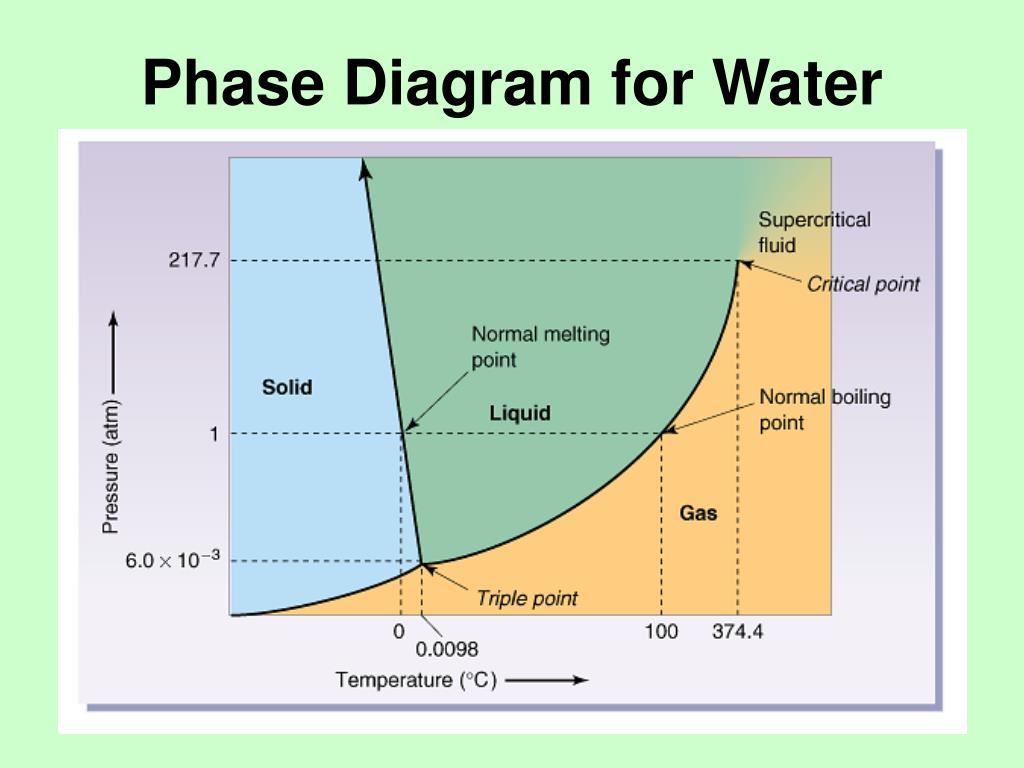
As we increase the temperature, the pressure of the water vapor increases, as described by the liquid-gas curve in the phase diagram for water ( Figure 10.31 ), and a two-phase equilibrium of liquid and gaseous phases remains. At a temperature of 374 °C, the vapor pressure has risen to 218 atm, and any further increase in temperature results.
Phase diagram and density of pure water in temperaturepressure space.... Download Scientific
Here, we compute the phase diagram of water at three hybrid DFT levels of theory (revPBE0-D3, PBE0-D3 and B3LYP-D3), accounting for thermal and nuclear fluctuations as well as proton disorder. We.